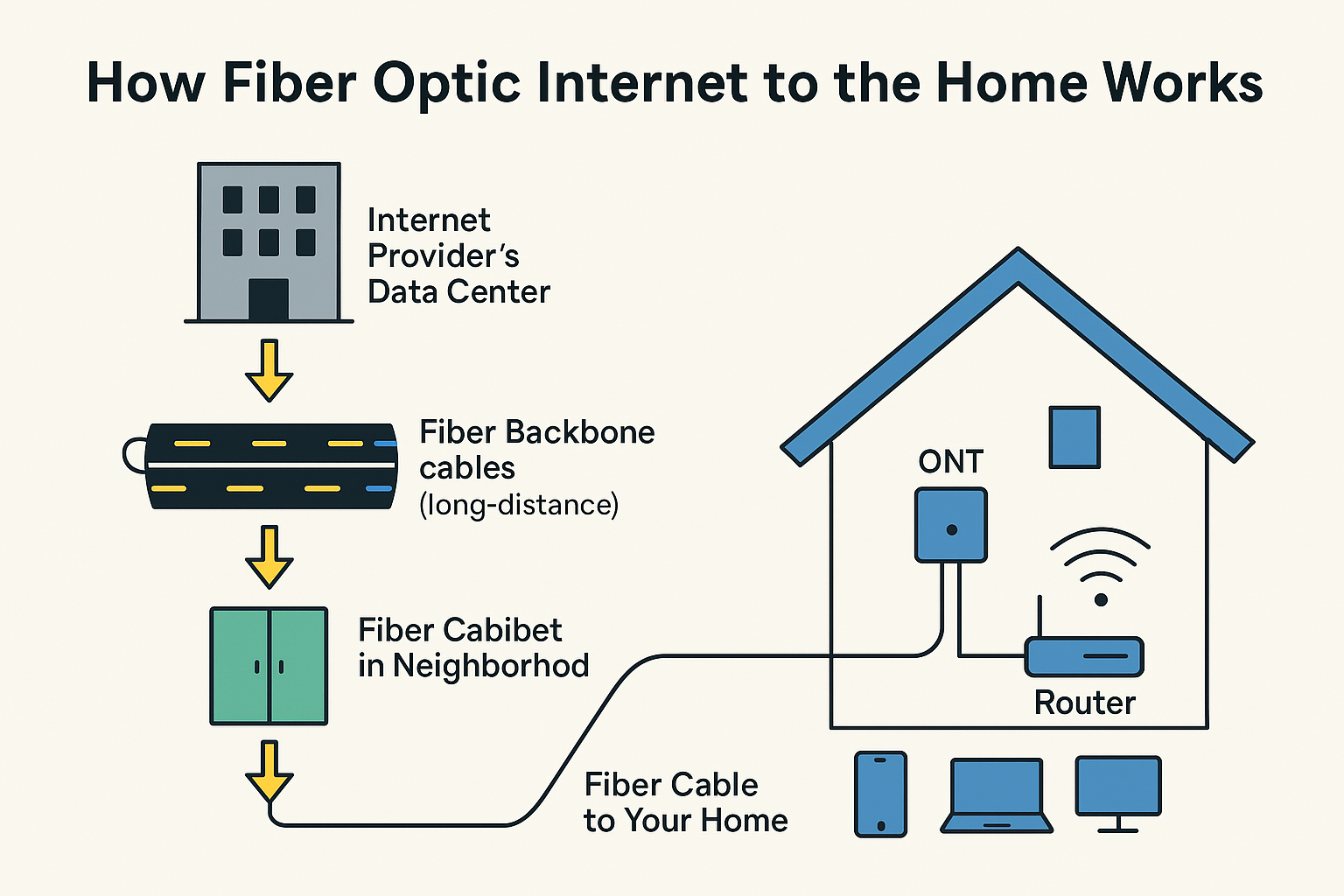
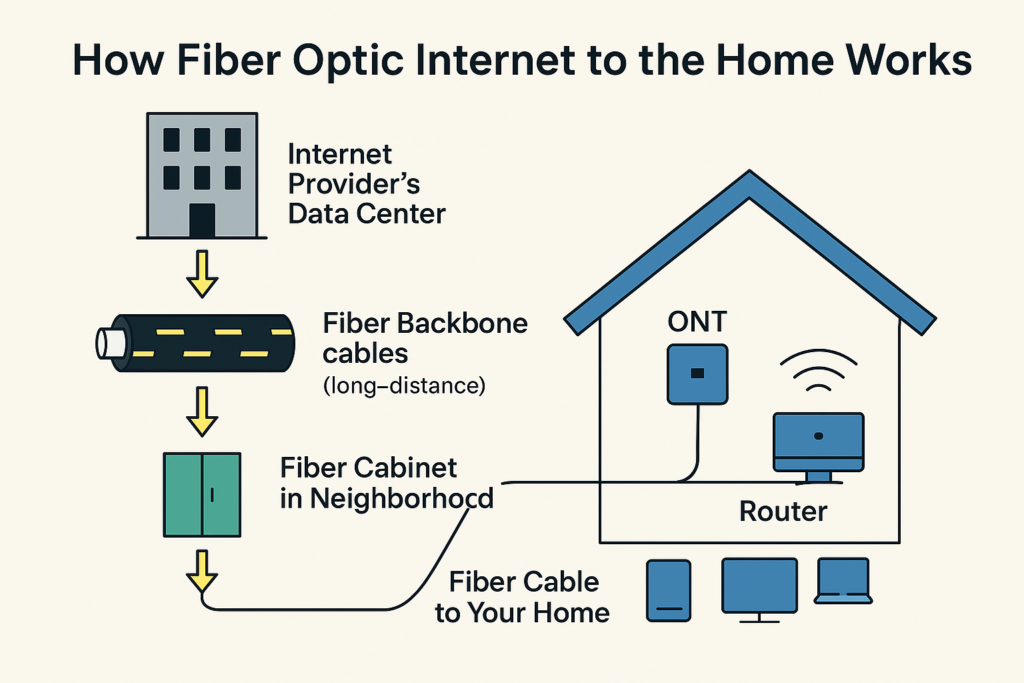
How Fiber Optic Internet to the Home Works (and Why It’s So Fast)
Fiber optic internet is the gold standard for fast, reliable connections—but how does it actually work? Let’s break it down in simple terms and visuals so you can understand what’s really happening when you stream a movie or utilize it to power the latest smart home integrations.
What Makes Fiber Optics Special?
Fiber optic cables don’t carry electricity—they carry light. That’s what makes them so powerful.
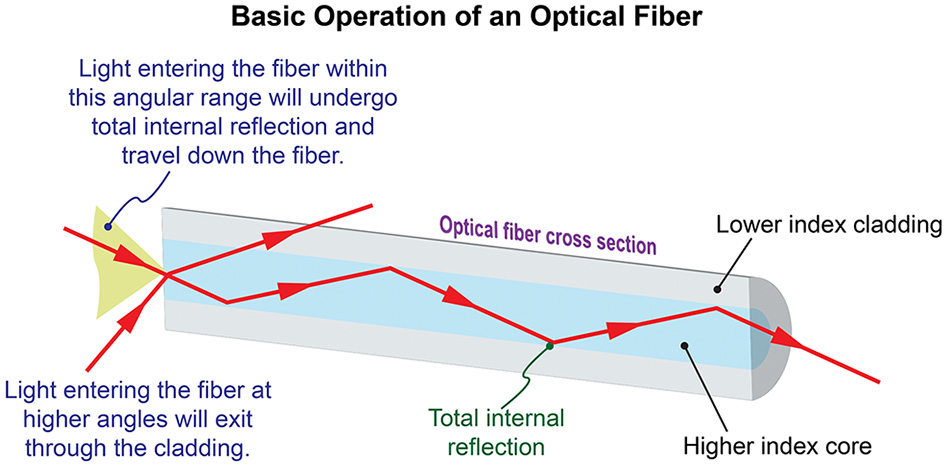
⚙️ How Fiber Cables Actually Work
Fiber optics use total internal reflection to bounce light through long strands of glass or plastic. These strands are bundled inside cables and wrapped in protective layers.
Think of it like this:
If you shine a laser pointer down a super clear, flexible straw, the light will keep bouncing and traveling forward without escaping. That’s basically how fiber works.
Inside a Fiber Optic Cable
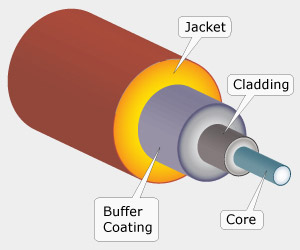
- Core (where the light travels)
- Cladding (keeps the light contained through reflection)
- Buffer Coating (protects from moisture and damage)
- Outer Jacket (durable exterior)
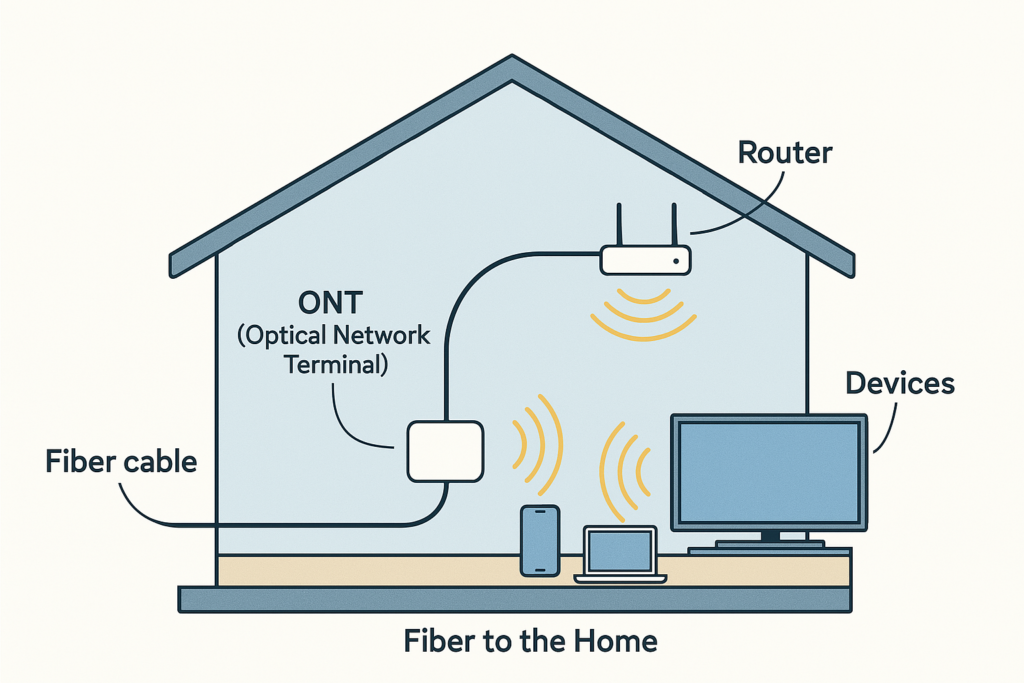
🏡 What Happens at Your House
Once the light signal reaches your home, it goes through a few more steps:
- ONT (Optical Network Terminal): Converts the light into digital signals your devices can understand.
- Router: Spreads the signal through Wi-Fi or ethernet inside your house.
- Devices: Your phone, TV, computer, and smart gadgets connect to the router.
🚀 Why Fiber is a Game-Changer
- ✅ Ultra-fast speeds (up to 10 Gbps and beyond)
- ✅ No slowdowns during peak hours
- ✅ Better for gaming, streaming, video calls, and smart homes
- ✅ Immune to electromagnetic interference
- ✅ Ready for future technology needs
Final Thoughts
Fiber internet is like having a digital expressway into your home. It’s fast, reliable, and designed for the demands of modern life. If you’ve got the option to upgrade to fiber, it’s one of the best tech investments you can make.